The 100 most commonly used verbs in the English Language
accept, allow, ask, believe, borrow, break, bring, buy, can/be able, cancel, change, clean, comb, complain, cough, count, cut, dance, draw, drink, drive, eat, explain, fall, fill, find, finish, fit, fix, fly, forget, give, go, have, hear, hurt, know, learn, leave, listen, live, look, lose, make/do, need, open
Parts Speech
Introductions
"Parts of speech" are the basic types of words that English has. Most grammar books say that there are eight parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, prepositions and interjections. We will add one more type: articles.
It is important to be able to recognize and identify the different types of words in English, so that you can understand grammar explanations and use the right word form in the right place. Here is a brief explanation of what the parts of speech are:
Noun
A noun is a naming word. It names a person, place, thing, idea, living creature, quality, or action. Examples:
cowboy, theatre, box, thought, tree, kindness, arrival
Verb
A verb is a word which describes an action (doing something) or a state (being something). Examples:
walk, talk, think, believe, live, like, want
Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun. Examples:
big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important
Adverb
An adverb is a word which usually describes a verb. It tells you how something is done. It may also tell you when or where something happened. Examples:
slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere
Pronoun
A pronoun is used instead of a noun, to avoid repeating the noun. Examples:
I, you, he, she, it, we, they
Conjunction
A conjunction joins two words, phrases or sentences together. Examples:
but, so, and, because, or
Preposition
A preposition usually comes before a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. It joins the noun to some other part of the sentence. Examples:
on, in, by, with, under, through, at
Interjection
An interjection is an unusual kind of word, because it often stands alone. Interjections are words which express emotion or surprise, and they are usually followed by exclamation marks. Examples:
Ouch!, Hello!, Hurray!, Oh no!, Ha!
Article
An article is used to introduce a noun. Examples:
the, a, an
More Than:
Parts Speech,Choose your level
Nouns

In English, there are two kinds of nouns: count nouns and non-count nouns. It is important to understand the difference between them, because they often use different articles, and non-count nouns usually have no plural. Here is a summary of the differences:
 - are things which can be counted. That means that there can be more than one of them. Also, when a count noun is singular and indefinite, the article "a/an" is often used with it. (The real meaning of "a" is "one".)
- are things which can be counted. That means that there can be more than one of them. Also, when a count noun is singular and indefinite, the article "a/an" is often used with it. (The real meaning of "a" is "one".)- are the names of things which can be counted.
 - are usually things which cannot be counted, such as rice or water. Non-count nouns have a singular form, but when they are indefinite, we either use the word "some" or nothing at all instead of an article.
- are usually things which cannot be counted, such as rice or water. Non-count nouns have a singular form, but when they are indefinite, we either use the word "some" or nothing at all instead of an article.- are the names of things or substances which can not be counted.
You can usually work out whether a noun is count or non-count by thinking about it. Count nouns are usually objects which can be counted. Non-count nouns are often substances (such as sand, water or rice) which cannot be easily counted, or they may be large abstract ideas such as "nature", "space" or "entertainment". Here are some more examples:
Examples:
Count Nouns: pen, table, car, idea, answer, class, exam, shoe...
-There are two books on the table.
-There is an elephent in my car.
Non-Count Nouns: education, intelligence, clothing, soap, air, cheese, grass, literature...
-Could i have some water please.
-I'd like rice with steak.
More than:
Count and non-count Nouns
Vietname
leovietname unit 70
quatao
Acctive/Passtive Overview
| Active | Passive | |
| Simple Present | Once a week, Tom cleans the house. | Once a week, the house is cleaned by Tom. |
| Present Continuous | Right now, Sarah is writing the letter. | Right now, the letter is being written by Sarah. |
| Simple Past | Sam repaired the car. | The car was repaired by Sam. |
| Past Continuous | The salesman was helping the customer when the thief came into the store. | The customer was being helped by the salesman when the thief came into the store. |
| Present Perfect | Many tourists have visited that castle. | That castle has been visited by many tourists. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Recently, John has been doing the work. | Recently, the work has been being done by John. |
| Past Perfect | George had repaired many cars before he received his mechanic's license. | Many cars had been repaired by George before he received his mechanic's license. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Chef Jones had been preparing the restaurant's fantastic dinners for two years before he moved to Paris. | The restaurant's fantastic dinners had been being prepared by Chef Jones for two years before he moved to Paris. |
| Simple Future will | Someone will finish the work by 5:00 PM. | The work will be finished by 5:00 PM. |
| Simple Future be going to | Sally is going to make a beautiful dinner tonight. | A beautiful dinner is going to be made by Sally tonight. |
| Future Continuous will | At 8:00 PM tonight, John will be washing the dishes. | At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes will be being washed by John. |
| Future Continuous be going to | At 8:00 PM tonight, John is going to be washing the dishes. | At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes are going to be being washed by John. |
| Future Perfect will | They will have completed the project before the deadline. | The project will have been completed before the deadline. |
| Future Perfect be going to | They are going to have completed the project before the deadline. | The project is going to have been completed before the deadline. |
| Future Perfect Continuous will | The famous artist will have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. | The mural will have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. |
| Future Perfect Continuous be going to | The famous artist is going to have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. | The mural is going to have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. |
| Used to | Jerry used to pay the bills. | The bills used to be paid by Jerry. |
| Would Always | My mother would always make the pies. | The pies would always be made by my mother. |
| Future in the Past Would | I knew John would finish the work by 5:00 PM. | I knew the work would be finished by 5:00 PM. |
| Future in the Past Was Going to | I thought Sally was going to make a beautiful dinner tonight. | I thought a beautiful dinner was going to be made by Sally tonight. |
Possessive Pronouns

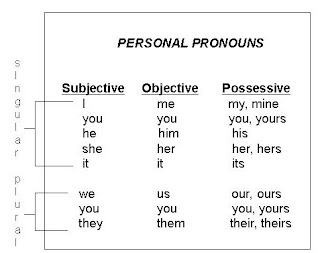
For examples:
J. What's your name?
G. Name! name! name! my name GoGo.
G. What's your name?
J. My name's Jeny.
J. Nice to meet you GoGo.
G. Nice to meet you, too.
G. Who's your friend?
J. This is Pod.
Q. Whose is this web site?
A. It's mine.
Q. Does Lynne own this web site?
A. Yes, it's hers.
Q. Does Lynne own the Internet?
A. No. It's ours.
- This money is yours.
- This car is hers.
- This computer is his.
- This house is theirs.
- This classroom is ours.

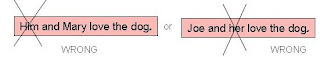
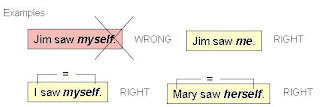
Note!
- I, me, he, she, him, her, you = a person
- you, we, us = people
- it = thing
- they, them = things or people
- my, your, his/her/its, our and their are possessive determiners (sometimes called possessive adjectives).
Learn more:
->View: Personal pronouns 1,Personal pronouns 2,Pronoun Case
->video: Possessive Pronouns,Suject and Object Pronouns,Pronouns
English Stories

Links on web
youtube, VOA News, Learn American English, British Council, UKGate, Learn English, Vocabulary, Wiki How, English Daily, The free dictionary, VDict, Multi Dictionary, English Page,Dictionary
Support
English lesson 1, 2, 3, ... form ThinkglishCoach- English lesson 1, Key vocabulary
- English lesson 2, Fruits & Vegetables
- English lesson 3, Driving a car
...
Learn English 01, 02, 03, ... form PodEnglish
Learn English 01, Introductions
Learn English 02, Time time time
Learn English 03, Familes
...
More than on Youtube.com
Vocabulary
Video
The Alphabet Song, The Alphabet Song
Colors, Colors Song, Colors, Colors song
Animals
food food
Things you can find in your closet.
The famous Santa Monica fruit market.
Driving a car
Asking and Giving Directions
25 actions
Like, love, Hates
Parts of the body
Telling times
Tools
Homes
Restaurant
Independence day
Go to the dinner
What do the British eat
12 steps to learn english conversation
Using Like
Introdutions
Learn & Enjoy it
Download vocabulary teacher count
BBC learn English
Learning English the fun ways
Multi vocabulary
Game
Kids games fun
Mistakes in english
American English Pronunciation
Lesson 1
Multi important
Fun easy english
Native Teacher
Computers
Download video
download all2convrt
A Year Plan For Learn English
The Goal For Learn English
We can speak English with anybody.
First Two Month
Start with picture dictionaries, study pronunciation, watch TV, listen to taped conversations, for two hours each day.
Second Two Month
Add grammar, Punctuation, spelling, vocabulary, studies, start to read newspaper/magazines, for two hours each day.
Third Two Month
Add one hour of English conversation classes everyday for two months, review grammar and vocabulary.
Fourth three Month
Learn hight level at the learn English center.
examples: ILA,...
Fifth three Month
Learn vocabulary, grammar, conversation... anywhere, any times and any topic.
After one year
Continuing education of fifth step(no schedule) and more than.
Question one: What free English learning resources are on the Internet?
Answer one:Links on the this page and multi page on the Internet.
Question two: What free English learning resources are available at the library, community or cultural center?
Answer two:I don't know.
Question three: What free English learning offer conversation class?
Answer three:I don't know.
Question four: What free English language exchange clubs offer conversation?
Answer four:I don't know.
Question five: Cost of books, texts, tapes, CD...?
Answer five:I don't know.
.........
Please, support me if you have other ideas or other thinks by comment or send to email.(si.huynhvn@gmail.com)
Line time: 20/august/2008 to 30/august/2008
We can speak English with anybody.
Form
First Two Month
Start with picture dictionaries, study pronunciation, watch TV, listen to taped conversations, for two hours each day.
Second Two Month
Add grammar, Punctuation, spelling, vocabulary, studies, start to read newspaper/magazines, for two hours each day.
Third Two Month
Add one hour of English conversation classes everyday for two months, review grammar and vocabulary.
Fourth three Month
Learn hight level at the learn English center.
examples: ILA,...
Fifth three Month
Learn vocabulary, grammar, conversation... anywhere, any times and any topic.
After one year
Continuing education of fifth step(no schedule) and more than.
Create a cost and benefit analysis for our plan
Question one: What free English learning resources are on the Internet?
Answer one:Links on the this page and multi page on the Internet.
Question two: What free English learning resources are available at the library, community or cultural center?
Answer two:I don't know.
Question three: What free English learning offer conversation class?
Answer three:I don't know.
Question four: What free English language exchange clubs offer conversation?
Answer four:I don't know.
Question five: Cost of books, texts, tapes, CD...?
Answer five:I don't know.
.........
Please, support me if you have other ideas or other thinks by comment or send to email.(si.huynhvn@gmail.com)
Time to prepare for the plan
Line time: 20/august/2008 to 30/august/2008
English Numbers And Alphablet
Numbers
Whole Numbers also known as Cardinal Numbers - used for counting
Ordinal Numbers - used for ranking
Fractions
Sums
What to say
Interesting Numbers
Click here for more
Alphabet
Learn English On line
You Tu Be
Types Of Verbs
Before you begin the verb tense lessons, it is extremely important to understand that NOT all English verbs are the same. English verbs are divided into three groups: Normal Verbs, Non-Continuous Verbs, and Mixed Verbs.
Group I Normal Verbs
Most verbs are "Normal Verbs." These verbs are usually physical actions which you can see somebody doing. These verbs can be used in all tenses.
Normal Verbs
to run, to walk, to eat, to fly, to go, to say, to touch, etc.
Examples:
* I eat dinner every day.
* I am eating dinner now.
Group II Non-Continuous Verbs
The second group, called "Non-Continuous Verbs," is smaller. These verbs are usually things you cannot see somebody doing. These verbs are rarely used in continuous tenses. They include:
Abstract Verbs
to be, to want, to cost, to seem, to need, to care, to contain, to owe, to exist...
Possession Verbs
to possess, to own, to belong...
Emotion Verbs
to like, to love, to hate, to dislike, to fear, to envy, to mind...
Examples:
* He is needing help now. Not Correct
* He needs help now. Correct
* He is wanting a drink now. Not Correct
* He wants a drink now. Correct
Group III Mixed Verbs
The third group, called "Mixed Verbs," is the smallest group. These verbs have more than one meaning. In a way, each meaning is a unique verb. Some meanings behave like "Non-Continuous Verbs," while other meanings behave like "Normal Verbs."
Mixed Verbs
to appear, to feel, to have, to hear, to look, to see, to weigh...
List of Mixed Verbs with Examples and Definitions:
to appear:
* Donna appears confused. Non-Continuous Verb
Donna seems confused.
* My favorite singer is appearing at the jazz club tonight. Normal Verb
My favorite singer is giving a performance at the jazz club tonight.
to have:
* I have a dollar now. Non-Continuous Verb
I possess a dollar.
* I am having fun now. Normal Verb
I am experiencing fun now.
to hear:
* She hears the music. Non-Continuous Verb
She hears the music with her ears.
* She is hearing voices. Normal Verb
She hears something others cannot hear. She is hearing voices in her mind.
to look:
* Nancy looks tired. Non-Continuous Verb
She seems tired.
* Farah is looking at the pictures. Normal Verb
She is looking with her eyes.
to miss:
* John misses Sally. Non-Continuous Verb
He is sad because she is not there.
* Debbie is missing her favorite TV program. Normal Verb
She is not there to see her favorite program.
to see:
* I see her. Non-Continuous Verb
I see her with my eyes.
* I am seeing the doctor. Normal Verb
I am visiting or consulting with a doctor. (Also used with dentist and lawyer.)
* I am seeing her. Normal Verb
I am having a relationship with her.
* He is seeing ghosts at night. Normal Verb
He sees something others cannot see. For example ghosts, aura, a vision of the future, etc.
to smell:
* The coffee smells good. Non-Continuous Verb
The coffee has a good smell.
* I am smelling the flowers. Normal Verb
I am sniffing the flowers to see what their smell is like.
to taste:
* The coffee tastes good. Non-Continuous Verb
The coffee has a good taste.
* I am tasting the cake. Normal Verb
I am trying the cake to see what it tastes like.
to think:
* He thinks the test is easy. Non-Continuous Verb
He considers the test to be easy.
* She is thinking about the question. Normal Verb
She is pondering the question, going over it in her mind.
to weigh:
* The table weighs a lot. Non-Continuous Verb
The table is heavy.
* She is weighing herself. Normal Verb
She is determining her weight.
Some Verbs Can Be Especially Confusing:
to be:
* Joe is American. Non-Continuous Verb
Joe is an American citizen.
* Joe is being very American. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving like a stereotypical American.
* Joe is being very rude. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving very rudely. Usually he is not rude.
* Joe is being very formal. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving very formally. Usually he is not formal.
NOTICE: Only rarely is "to be" used in a continuous form. This is most commonly done when a person is temporarily behaving badly or stereotypically. It can also be used when someone's behavior is noticeably different.
to feel:
* The massage feels great. Non-Continuous Verb
The massage has a pleasing feeling.
* I don't feel well today. Sometimes used as Non-Continuous Verb
I am a little sick.
I am not feeling well today. Sometimes used as Normal Verb
I am a little sick.
NOTICE: The second meaning of "feel" is very flexible and there is no real difference in meaning between "I don't feel well today" and "I am not feeling well today."
Group I Normal Verbs
Most verbs are "Normal Verbs." These verbs are usually physical actions which you can see somebody doing. These verbs can be used in all tenses.
Normal Verbs
to run, to walk, to eat, to fly, to go, to say, to touch, etc.
Examples:
* I eat dinner every day.
* I am eating dinner now.
Group II Non-Continuous Verbs
The second group, called "Non-Continuous Verbs," is smaller. These verbs are usually things you cannot see somebody doing. These verbs are rarely used in continuous tenses. They include:
Abstract Verbs
to be, to want, to cost, to seem, to need, to care, to contain, to owe, to exist...
Possession Verbs
to possess, to own, to belong...
Emotion Verbs
to like, to love, to hate, to dislike, to fear, to envy, to mind...
Examples:
* He is needing help now. Not Correct
* He needs help now. Correct
* He is wanting a drink now. Not Correct
* He wants a drink now. Correct
Group III Mixed Verbs
The third group, called "Mixed Verbs," is the smallest group. These verbs have more than one meaning. In a way, each meaning is a unique verb. Some meanings behave like "Non-Continuous Verbs," while other meanings behave like "Normal Verbs."
Mixed Verbs
to appear, to feel, to have, to hear, to look, to see, to weigh...
List of Mixed Verbs with Examples and Definitions:
to appear:
* Donna appears confused. Non-Continuous Verb
Donna seems confused.
* My favorite singer is appearing at the jazz club tonight. Normal Verb
My favorite singer is giving a performance at the jazz club tonight.
to have:
* I have a dollar now. Non-Continuous Verb
I possess a dollar.
* I am having fun now. Normal Verb
I am experiencing fun now.
to hear:
* She hears the music. Non-Continuous Verb
She hears the music with her ears.
* She is hearing voices. Normal Verb
She hears something others cannot hear. She is hearing voices in her mind.
to look:
* Nancy looks tired. Non-Continuous Verb
She seems tired.
* Farah is looking at the pictures. Normal Verb
She is looking with her eyes.
to miss:
* John misses Sally. Non-Continuous Verb
He is sad because she is not there.
* Debbie is missing her favorite TV program. Normal Verb
She is not there to see her favorite program.
to see:
* I see her. Non-Continuous Verb
I see her with my eyes.
* I am seeing the doctor. Normal Verb
I am visiting or consulting with a doctor. (Also used with dentist and lawyer.)
* I am seeing her. Normal Verb
I am having a relationship with her.
* He is seeing ghosts at night. Normal Verb
He sees something others cannot see. For example ghosts, aura, a vision of the future, etc.
to smell:
* The coffee smells good. Non-Continuous Verb
The coffee has a good smell.
* I am smelling the flowers. Normal Verb
I am sniffing the flowers to see what their smell is like.
to taste:
* The coffee tastes good. Non-Continuous Verb
The coffee has a good taste.
* I am tasting the cake. Normal Verb
I am trying the cake to see what it tastes like.
to think:
* He thinks the test is easy. Non-Continuous Verb
He considers the test to be easy.
* She is thinking about the question. Normal Verb
She is pondering the question, going over it in her mind.
to weigh:
* The table weighs a lot. Non-Continuous Verb
The table is heavy.
* She is weighing herself. Normal Verb
She is determining her weight.
Some Verbs Can Be Especially Confusing:
to be:
* Joe is American. Non-Continuous Verb
Joe is an American citizen.
* Joe is being very American. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving like a stereotypical American.
* Joe is being very rude. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving very rudely. Usually he is not rude.
* Joe is being very formal. Normal Verb
Joe is behaving very formally. Usually he is not formal.
NOTICE: Only rarely is "to be" used in a continuous form. This is most commonly done when a person is temporarily behaving badly or stereotypically. It can also be used when someone's behavior is noticeably different.
to feel:
* The massage feels great. Non-Continuous Verb
The massage has a pleasing feeling.
* I don't feel well today. Sometimes used as Non-Continuous Verb
I am a little sick.
I am not feeling well today. Sometimes used as Normal Verb
I am a little sick.
NOTICE: The second meaning of "feel" is very flexible and there is no real difference in meaning between "I don't feel well today" and "I am not feeling well today."
Future Perfect Continuous
Future Perfect Continuous has two different forms: "will have been doing " and "be going to have been doing." Unlike Simple Future forms, Future Perfect Continuous forms are usually interchangeable.
FORM Future Perfect Continuous with "Will"
[will have been + present participle]
Examples:
* You will have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
* Will you have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives?
* You will not have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
FORM Future Perfect Continuous with "Be Going To"
[am/is/are + going to have been + present participle]
Examples:
* You are going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
* Are you going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives?
* You are not going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
NOTE: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Perfect Continuous with little or no difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Perfect Continuous Forms
USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Future
We use the Future Perfect Continuous to show that something will continue up until a particular event or time in the future. "For five minutes," "for two weeks," and "since Friday" are all durations which can be used with the Future Perfect Continuous. Notice that this is related to the Present Perfect Continuous and the Past Perfect Continuous; however, with Future Perfect Continuous, the duration stops at or before a reference point in the future.
Examples:
* They will have been talking for over an hour by the time Thomas arrives.
* She is going to have been working at that company for three years when it finally closes.
* James will have been teaching at the university for more than a year by the time he leaves for Asia.
* How long will you have been studying when you graduate?
* We are going to have been driving for over three days straight when we get to Anchorage.
* A: When you finish your English course, will you have been living in New Zealand for over a year?
B: No, I will not have been living here that long.
Notice in the examples above that the reference points (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because these future events are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Cause of Something in the Future
Using the Future Perfect Continuous before another action in the future is a good way to show cause and effect.
Examples:
* Jason will be tired when he gets home because he will have been jogging for over an hour.
* Claudia's English will be perfect when she returns to Germany because she is going to have been studying English in the United States for over two years.
Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect Continuous
If you do not include a duration such as "for five minutes," "for two weeks" or "since Friday," many English speakers choose to use the Future Continuous rather than the Future Perfect Continuous. Be careful because this can change the meaning of the sentence. Future Continuous emphasizes interrupted actions, whereas Future Perfect Continuous emphasizes a duration of time before something in the future. Study the examples below to understand the difference.
Examples:
* He will be tired because he will be exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he will be tired because he will be exercising at that exact moment in the future.
* He will be tired because he will have been exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he will be tired because he will have been exercising for a period of time. It is possible that he will still be exercising at that moment OR that he will just have finished.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Future Perfect Continuous cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Perfect Continuous, Present Perfect Continuous is used.
Examples:
* You won't get a promotion until you will have been working here as long as Tim. Not Correct
* You won't get a promotion until you have been working here as long as Tim. Correct
AND REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Future Perfect Continuous with these verbs, you must use Future Perfect .
Examples:
* Ned will have been having his driver's license for over two years. Not Correct
* Ned will have had his driver's license for over two years. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will only have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives.
* Will you only have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives?
* You are only going to have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives.
* Are you only going to have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* The famous artist will have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. Active
* The mural will have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. Passive
* The famous artist is going to have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. Active
* The mural is going to have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Future Perfect Continuous are not common.
More view click here
FORM Future Perfect Continuous with "Will"
[will have been + present participle]
Examples:
* You will have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
* Will you have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives?
* You will not have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
FORM Future Perfect Continuous with "Be Going To"
[am/is/are + going to have been + present participle]
Examples:
* You are going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
* Are you going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives?
* You are not going to have been waiting for more than two hours when her plane finally arrives.
NOTE: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Perfect Continuous with little or no difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Perfect Continuous Forms
USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Future
We use the Future Perfect Continuous to show that something will continue up until a particular event or time in the future. "For five minutes," "for two weeks," and "since Friday" are all durations which can be used with the Future Perfect Continuous. Notice that this is related to the Present Perfect Continuous and the Past Perfect Continuous; however, with Future Perfect Continuous, the duration stops at or before a reference point in the future.
Examples:
* They will have been talking for over an hour by the time Thomas arrives.
* She is going to have been working at that company for three years when it finally closes.
* James will have been teaching at the university for more than a year by the time he leaves for Asia.
* How long will you have been studying when you graduate?
* We are going to have been driving for over three days straight when we get to Anchorage.
* A: When you finish your English course, will you have been living in New Zealand for over a year?
B: No, I will not have been living here that long.
Notice in the examples above that the reference points (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because these future events are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Cause of Something in the Future
Using the Future Perfect Continuous before another action in the future is a good way to show cause and effect.
Examples:
* Jason will be tired when he gets home because he will have been jogging for over an hour.
* Claudia's English will be perfect when she returns to Germany because she is going to have been studying English in the United States for over two years.
Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect Continuous
If you do not include a duration such as "for five minutes," "for two weeks" or "since Friday," many English speakers choose to use the Future Continuous rather than the Future Perfect Continuous. Be careful because this can change the meaning of the sentence. Future Continuous emphasizes interrupted actions, whereas Future Perfect Continuous emphasizes a duration of time before something in the future. Study the examples below to understand the difference.
Examples:
* He will be tired because he will be exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he will be tired because he will be exercising at that exact moment in the future.
* He will be tired because he will have been exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he will be tired because he will have been exercising for a period of time. It is possible that he will still be exercising at that moment OR that he will just have finished.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Future Perfect Continuous cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Perfect Continuous, Present Perfect Continuous is used.
Examples:
* You won't get a promotion until you will have been working here as long as Tim. Not Correct
* You won't get a promotion until you have been working here as long as Tim. Correct
AND REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Future Perfect Continuous with these verbs, you must use Future Perfect .
Examples:
* Ned will have been having his driver's license for over two years. Not Correct
* Ned will have had his driver's license for over two years. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will only have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives.
* Will you only have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives?
* You are only going to have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives.
* Are you only going to have been waiting for a few minutes when her plane arrives?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* The famous artist will have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. Active
* The mural will have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. Passive
* The famous artist is going to have been painting the mural for over six months by the time it is finished. Active
* The mural is going to have been being painted by the famous artist for over six months by the time it is finished. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Future Perfect Continuous are not common.
More view click here
Future Pefect
Future Perfect has two different forms: "will have done" and "be going to have done." Unlike Simple Future forms, Future Perfect forms are usually interchangeable.
FORM Future Perfect with "Will"
[will have + past participle]
Examples:
* You will have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
* Will you have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
* You will not have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
FORM Future Perfect with "Be Going To"
[am/is/are + going to have + past participle]
Examples:
* You are going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
* Are you going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
* You are not going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
NOTE: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Perfect with little or no difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Perfect Forms
USE 1 Completed Action Before Something in the Future
The Future Perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
Examples:
* By next November, I will have received my promotion.
* By the time he gets home, she is going to have cleaned the entire house.
* I am not going to have finished this test by 3 o'clock.
* Will she have learned enough Chinese to communicate before she moves to Beijing?
* Sam is probably going to have completed the proposal by the time he leaves this afternoon.
* By the time I finish this course, I will have taken ten tests.
* How many countries are you going to have visited by the time you turn 50?
Notice in the examples above that the reference points (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because the interruptions are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Duration Before Something in the Future (Non-Continuous Verbs)
With Non-Continuous Verbs and some non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, we use the Future Perfect to show that something will continue up until another action in the future.
Examples:
* I will have been in London for six months by the time I leave.
* By Monday, Susan is going to have had my book for a week.
Although the above use of Future Perfect is normally limited to Non-Continuous Verbs and non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, the words "live," "work," "teach," and "study" are sometimes used in this way even though they are NOT Non-Continuous Verbs.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Future Perfect cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Perfect, Present Perfect is used.
Examples:
* I am going to see a movie when I will have finished my homework. Not Correct
* I am going to see a movie when I have finished my homework. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will only have learned a few words.
* Will you only have learned a few words?
* You are only going to have learned a few words.
* Are you only going to have learned a few words?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* They will have completed the project before the deadline. Active
* The project will have been completed before the deadline. Passive
* They are going to have completed the project before the deadline. Active
* The project is going to have been completed before the deadline. Passive
More view click here
FORM Future Perfect with "Will"
[will have + past participle]
Examples:
* You will have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
* Will you have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
* You will not have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
FORM Future Perfect with "Be Going To"
[am/is/are + going to have + past participle]
Examples:
* You are going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
* Are you going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.?
* You are not going to have perfected your English by the time you come back from the U.S.
NOTE: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Perfect with little or no difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Perfect Forms
USE 1 Completed Action Before Something in the Future
The Future Perfect expresses the idea that something will occur before another action in the future. It can also show that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
Examples:
* By next November, I will have received my promotion.
* By the time he gets home, she is going to have cleaned the entire house.
* I am not going to have finished this test by 3 o'clock.
* Will she have learned enough Chinese to communicate before she moves to Beijing?
* Sam is probably going to have completed the proposal by the time he leaves this afternoon.
* By the time I finish this course, I will have taken ten tests.
* How many countries are you going to have visited by the time you turn 50?
Notice in the examples above that the reference points (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because the interruptions are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Duration Before Something in the Future (Non-Continuous Verbs)
With Non-Continuous Verbs and some non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, we use the Future Perfect to show that something will continue up until another action in the future.
Examples:
* I will have been in London for six months by the time I leave.
* By Monday, Susan is going to have had my book for a week.
Although the above use of Future Perfect is normally limited to Non-Continuous Verbs and non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, the words "live," "work," "teach," and "study" are sometimes used in this way even though they are NOT Non-Continuous Verbs.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Future Perfect cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Perfect, Present Perfect is used.
Examples:
* I am going to see a movie when I will have finished my homework. Not Correct
* I am going to see a movie when I have finished my homework. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will only have learned a few words.
* Will you only have learned a few words?
* You are only going to have learned a few words.
* Are you only going to have learned a few words?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* They will have completed the project before the deadline. Active
* The project will have been completed before the deadline. Passive
* They are going to have completed the project before the deadline. Active
* The project is going to have been completed before the deadline. Passive
More view click here
Future Continuous
Future Continuous has two different forms: "will be doing " and "be going to be doing." Unlike Simple Future forms, Future Continuous forms are usually interchangeable.
FORM Future Continuous with "Will"
[will be + present participle]
Examples:
* You will be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
* Will you be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight?
* You will not be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
FORM Future Continuous with "Be Going To "
[am/is/are + going to be + present participle]
Examples:
* You are going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
* Are you going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight?
* You are not going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
REMEMBER: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Continuous with little difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Continuous Forms
USE 1 Interrupted Action in the Future
Use the Future Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Examples:
* I will be watching TV when she arrives tonight.
* I will be waiting for you when your bus arrives.
* I am going to be staying at the Madison Hotel, if anything happens and you need to contact me.
* He will be studying at the library tonight, so he will not see Jennifer when she arrives.
Notice in the examples above that the interruptions (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because the interruptions are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Specific Time as an Interruption in the Future
In USE 1, described above, the Future Continuous is interrupted by a short action in the future. In addition to using short actions as interruptions, you can also use a specific time as an interruption.
Examples:
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to be eating dinner.
I will be in the process of eating dinner.
* At midnight tonight, we will still be driving through the desert.
We will be in the process of driving through the desert.
REMEMBER
In the Simple Future, a specific time is used to show the time an action will begin or end. In the Future Continuous, a specific time interrupts the action.
Examples:
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to eat dinner.
I am going to start eating at 6 PM.
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to be eating dinner.
I am going to start earlier and I will be in the process of eating dinner at 6 PM.
USE 3 Parallel Actions in the Future
When you use the Future Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions will be happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.
Examples:
* I am going to be studying and he is going to be making dinner.
* Tonight, they will be eating dinner, discussing their plans, and having a good time.
* While Ellen is reading, Tim will be watching television.
Notice "is reading" because of the time clause containing "while." (See Explanation Below)
USE 4 Atmosphere in the Future
In English, we often use a series of Parallel Actions to describe atmosphere at a specific point in the future.
Example:
* When I arrive at the party, everybody is going to be celebrating. Some will be dancing. Others are going to be talking. A few people will be eating pizza, and several people are going to be drinking beer. They always do the same thing.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future tenses, the Future Continuous cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Continuous, Present Continuous is used.
Examples:
* While I am going to be finishing my homework, she is going to make dinner. Not Correct
* While I am finishing my homework, she is going to make dinner. Correct
AND REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Future Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Future.
Examples:
* Jane will be being at my house when you arrive. Not Correct
* Jane will be at my house when you arrive. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will still be waiting for her when her plane arrives.
* Will you still be waiting for her when her plane arrives?
* You are still going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives.
* Are you still going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* At 8:00 PM tonight, John will be washing the dishes. Active
* At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes will be being washed by John. Passive
* At 8:00 PM tonight, John is going to be washing the dishes. Active
* At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes are going to be being washed by John. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Future Continuous are not common.
More view click here
FORM Future Continuous with "Will"
[will be + present participle]
Examples:
* You will be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
* Will you be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight?
* You will not be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
FORM Future Continuous with "Be Going To "
[am/is/are + going to be + present participle]
Examples:
* You are going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
* Are you going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight?
* You are not going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives tonight.
REMEMBER: It is possible to use either "will" or "be going to" to create the Future Continuous with little difference in meaning.
Complete List of Future Continuous Forms
USE 1 Interrupted Action in the Future
Use the Future Continuous to indicate that a longer action in the future will be interrupted by a shorter action in the future. Remember this can be a real interruption or just an interruption in time.
Examples:
* I will be watching TV when she arrives tonight.
* I will be waiting for you when your bus arrives.
* I am going to be staying at the Madison Hotel, if anything happens and you need to contact me.
* He will be studying at the library tonight, so he will not see Jennifer when she arrives.
Notice in the examples above that the interruptions (marked in italics) are in Simple Present rather than Simple Future. This is because the interruptions are in time clauses, and you cannot use future tenses in time clauses.
USE 2 Specific Time as an Interruption in the Future
In USE 1, described above, the Future Continuous is interrupted by a short action in the future. In addition to using short actions as interruptions, you can also use a specific time as an interruption.
Examples:
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to be eating dinner.
I will be in the process of eating dinner.
* At midnight tonight, we will still be driving through the desert.
We will be in the process of driving through the desert.
REMEMBER
In the Simple Future, a specific time is used to show the time an action will begin or end. In the Future Continuous, a specific time interrupts the action.
Examples:
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to eat dinner.
I am going to start eating at 6 PM.
* Tonight at 6 PM, I am going to be eating dinner.
I am going to start earlier and I will be in the process of eating dinner at 6 PM.
USE 3 Parallel Actions in the Future
When you use the Future Continuous with two actions in the same sentence, it expresses the idea that both actions will be happening at the same time. The actions are parallel.
Examples:
* I am going to be studying and he is going to be making dinner.
* Tonight, they will be eating dinner, discussing their plans, and having a good time.
* While Ellen is reading, Tim will be watching television.
Notice "is reading" because of the time clause containing "while." (See Explanation Below)
USE 4 Atmosphere in the Future
In English, we often use a series of Parallel Actions to describe atmosphere at a specific point in the future.
Example:
* When I arrive at the party, everybody is going to be celebrating. Some will be dancing. Others are going to be talking. A few people will be eating pizza, and several people are going to be drinking beer. They always do the same thing.
REMEMBER No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future tenses, the Future Continuous cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Future Continuous, Present Continuous is used.
Examples:
* While I am going to be finishing my homework, she is going to make dinner. Not Correct
* While I am finishing my homework, she is going to make dinner. Correct
AND REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Future Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Future.
Examples:
* Jane will be being at my house when you arrive. Not Correct
* Jane will be at my house when you arrive. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will still be waiting for her when her plane arrives.
* Will you still be waiting for her when her plane arrives?
* You are still going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives.
* Are you still going to be waiting for her when her plane arrives?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* At 8:00 PM tonight, John will be washing the dishes. Active
* At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes will be being washed by John. Passive
* At 8:00 PM tonight, John is going to be washing the dishes. Active
* At 8:00 PM tonight, the dishes are going to be being washed by John. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Future Continuous are not common.
More view click here
Simple Future
Simple Future has two different forms in English: "will" and "be going to." Although the two forms can sometimes be used interchangeably, they often express two very different meanings. These different meanings might seem too abstract at first, but with time and practice, the differences will become clear. Both "will" and "be going to" refer to a specific time in the future.
FORM Will
[will + verb]
Examples:
* You will help him later.
* Will you help him later?
* You will not help him later.
FORM Be Going To
[am/is/are + going to + verb]
Examples:
* You are going to meet Jane tonight.
* Are you going to meet Jane tonight?
* You are not going to meet Jane tonight.
USE 1 "Will" to Express a Voluntary Action
"Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do something for us. Similarly, we use "will not" or "won't" when we refuse to voluntarily do something.
Examples:
* I will send you the information when I get it.
* I will translate the email, so Mr. Smith can read it.
* Will you help me move this heavy table?
* Will you make dinner?
* I will not do your homework for you.
* I won't do all the housework myself!
* A: I'm really hungry.
B: I'll make some sandwiches.
* A: I'm so tired. I'm about to fall asleep.
B: I'll get you some coffee.
* A: The phone is ringing.
B: I'll get it.
USE 2 "Will" to Express a Promise
"Will" is usually used in promises.
Examples:
* I will call you when I arrive.
* If I am elected President of the United States, I will make sure everyone has access to inexpensive health insurance.
* I promise I will not tell him about the surprise party.
* Don't worry, I'll be careful.
* I won't tell anyone your secret.
USE 3 "Be going to" to Express a Plan
"Be going to" expresses that something is a plan. It expresses the idea that a person intends to do something in the future. It does not matter whether the plan is realistic or not.
Examples:
* He is going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
* She is not going to spend her vacation in Hawaii.
* A: When are we going to meet each other tonight?
B: We are going to meet at 6 PM.
* I'm going to be an actor when I grow up.
* Michelle is going to begin medical school next year.
* They are going to drive all the way to Alaska.
* Who are you going to invite to the party?
* A: Who is going to make John's birthday cake?
B: Sue is going to make John's birthday cake.
USE 4 "Will" or "Be Going to" to Express a Prediction
Both "will" and "be going to" can express the idea of a general prediction about the future. Predictions are guesses about what might happen in the future. In "prediction" sentences, the subject usually has little control over the future and therefore USES 1-3 do not apply. In the following examples, there is no difference in meaning.
Examples:
* The year 2222 will be a very interesting year.
* The year 2222 is going to be a very interesting year.
* John Smith will be the next President.
* John Smith is going to be the next President.
* The movie "Zenith" will win several Academy Awards.
* The movie "Zenith" is going to win several Academy Awards.
IMPORTANT
In the Simple Future, it is not always clear which USE the speaker has in mind. Often, there is more than one way to interpret a sentence's meaning.
No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Simple Future cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Simple Future, Simple Present is used.
Examples:
* When you will arrive tonight, we will go out for dinner. Not Correct
* When you arrive tonight, we will go out for dinner. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will never help him.
* Will you ever help him?
* You are never going to meet Jane.
* Are you ever going to meet Jane?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* John will finish the work by 5:00 PM. Active
* The work will be finished by 5:00 PM. Passive
* Sally is going to make a beautiful dinner tonight. Active
* A beautiful dinner is going to be made by Sally tonight. Passive
More view click here
FORM Will
[will + verb]
Examples:
* You will help him later.
* Will you help him later?
* You will not help him later.
FORM Be Going To
[am/is/are + going to + verb]
Examples:
* You are going to meet Jane tonight.
* Are you going to meet Jane tonight?
* You are not going to meet Jane tonight.
USE 1 "Will" to Express a Voluntary Action
"Will" often suggests that a speaker will do something voluntarily. A voluntary action is one the speaker offers to do for someone else. Often, we use "will" to respond to someone else's complaint or request for help. We also use "will" when we request that someone help us or volunteer to do something for us. Similarly, we use "will not" or "won't" when we refuse to voluntarily do something.
Examples:
* I will send you the information when I get it.
* I will translate the email, so Mr. Smith can read it.
* Will you help me move this heavy table?
* Will you make dinner?
* I will not do your homework for you.
* I won't do all the housework myself!
* A: I'm really hungry.
B: I'll make some sandwiches.
* A: I'm so tired. I'm about to fall asleep.
B: I'll get you some coffee.
* A: The phone is ringing.
B: I'll get it.
USE 2 "Will" to Express a Promise
"Will" is usually used in promises.
Examples:
* I will call you when I arrive.
* If I am elected President of the United States, I will make sure everyone has access to inexpensive health insurance.
* I promise I will not tell him about the surprise party.
* Don't worry, I'll be careful.
* I won't tell anyone your secret.
USE 3 "Be going to" to Express a Plan
"Be going to" expresses that something is a plan. It expresses the idea that a person intends to do something in the future. It does not matter whether the plan is realistic or not.
Examples:
* He is going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
* She is not going to spend her vacation in Hawaii.
* A: When are we going to meet each other tonight?
B: We are going to meet at 6 PM.
* I'm going to be an actor when I grow up.
* Michelle is going to begin medical school next year.
* They are going to drive all the way to Alaska.
* Who are you going to invite to the party?
* A: Who is going to make John's birthday cake?
B: Sue is going to make John's birthday cake.
USE 4 "Will" or "Be Going to" to Express a Prediction
Both "will" and "be going to" can express the idea of a general prediction about the future. Predictions are guesses about what might happen in the future. In "prediction" sentences, the subject usually has little control over the future and therefore USES 1-3 do not apply. In the following examples, there is no difference in meaning.
Examples:
* The year 2222 will be a very interesting year.
* The year 2222 is going to be a very interesting year.
* John Smith will be the next President.
* John Smith is going to be the next President.
* The movie "Zenith" will win several Academy Awards.
* The movie "Zenith" is going to win several Academy Awards.
IMPORTANT
In the Simple Future, it is not always clear which USE the speaker has in mind. Often, there is more than one way to interpret a sentence's meaning.
No Future in Time Clauses
Like all future forms, the Simple Future cannot be used in clauses beginning with time expressions such as: when, while, before, after, by the time, as soon as, if, unless, etc. Instead of Simple Future, Simple Present is used.
Examples:
* When you will arrive tonight, we will go out for dinner. Not Correct
* When you arrive tonight, we will go out for dinner. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You will never help him.
* Will you ever help him?
* You are never going to meet Jane.
* Are you ever going to meet Jane?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* John will finish the work by 5:00 PM. Active
* The work will be finished by 5:00 PM. Passive
* Sally is going to make a beautiful dinner tonight. Active
* A beautiful dinner is going to be made by Sally tonight. Passive
More view click here
Present Perfect Continuous
[has/have + been + present participle]
Examples:
* You have been waiting here for two hours.
* Have you been waiting here for two hours?
* You have not been waiting here for two hours.
USE 1 Duration from the Past Until Now
We use the Present Perfect Continuous to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now. "For five minutes," "for two weeks," and "since Tuesday" are all durations which can be used with the Present Perfect Continuous.
Examples:
* They have been talking for the last hour.
* She has been working at that company for three years.
* What have you been doing for the last 30 minutes?
* James has been teaching at the university since June.
* We have been waiting here for over two hours!
* Why has Nancy not been taking her medicine for the last three days?
USE 2 Recently, Lately
You can also use the Present Perfect Continuous WITHOUT a duration such as "for two weeks." Without the duration, the tense has a more general meaning of "lately." We often use the words "lately" or "recently" to emphasize this meaning.
Examples:
* Recently, I have been feeling really tired.
* She has been watching too much television lately.
* Have you been exercising lately?
* Mary has been feeling a little depressed.
* Lisa has not been practicing her English.
* What have you been doing?
IMPORTANT
Remember that the Present Perfect Continuous has the meaning of "lately" or "recently." If you use the Present Perfect Continuous in a question such as "Have you been feeling alright?", it can suggest that the person looks sick or unhealthy. A question such as "Have you been smoking?" can suggest that you smell the smoke on the person. Using this tense in a question suggests you can see, smell, hear or feel the results of the action. It is possible to insult someone by using this tense incorrectly.
REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs/ Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Present Perfect Continuous with these verbs, you must use Present Perfect.
Examples:
* Sam has been having his car for two years. Not Correct
* Sam has had his car for two years. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You have only been waiting here for one hour.
* Have you only been waiting here for one hour?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Recently, John has been doing the work. Active
* Recently, the work has been being done by John. Passive
NOTE: Present Perfect Continuous is less commonly used in its passive form.
More view click here
Present Perfect
[has/have + past participle]
Examples:
* You have seen that movie many times.
* Have you seen that movie many times?
* You have not seen that movie many times.
USE 1 Unspecified Time Before Now
We use the Present Perfect to say that an action happened at an unspecified time before now. The exact time is not important. You CANNOT use the Present Perfect with specific time expressions such as: yesterday, one year ago, last week, when I was a child, when I lived in Japan, at that moment, that day, one day, etc. We CAN use the Present Perfect with unspecific expressions such as: ever, never, once, many times, several times, before, so far, already, yet, etc.
Examples:
* I have seen that movie twenty times.
* I think I have met him once before.
* There have been many earthquakes in California.
* People have traveled to the Moon.
* People have not traveled to Mars.
* Have you read the book yet?
* Nobody has ever climbed that mountain.
* A: Has there ever been a war in the United States?
B: Yes, there has been a war in the United States.
How Do You Actually Use the Present Perfect?
The concept of "unspecified time" can be very confusing to English learners. It is best to associate Present Perfect with the following topics:
TOPIC 1 Experience
You can use the Present Perfect to describe your experience. It is like saying, "I have the experience of..." You can also use this tense to say that you have never had a certain experience. The Present Perfect is NOT used to describe a specific event.
Examples:
* I have been to France.
This sentence means that you have had the experience of being in France. Maybe you have been there once, or several times.
* I have been to France three times.
You can add the number of times at the end of the sentence.
* I have never been to France.
This sentence means that you have not had the experience of going to France.
* I think I have seen that movie before.
* He has never traveled by train.
* Joan has studied two foreign languages.
* A: Have you ever met him?
B: No, I have not met him.
TOPIC 2 Change Over Time
We often use the Present Perfect to talk about change that has happened over a period of time.
Examples:
* You have grown since the last time I saw you.
* The government has become more interested in arts education.
* Japanese has become one of the most popular courses at the university since the Asian studies program was established.
* My English has really improved since I moved to Australia.
TOPIC 3 Accomplishments
We often use the Present Perfect to list the accomplishments of individuals and humanity. You cannot mention a specific time.
Examples:
* Man has walked on the Moon.
* Our son has learned how to read.
* Doctors have cured many deadly diseases.
* Scientists have split the atom.
TOPIC 4 An Uncompleted Action You Are Expecting
We often use the Present Perfect to say that an action which we expected has not happened. Using the Present Perfect suggests that we are still waiting for the action to happen.
Examples:
* James has not finished his homework yet.
* Susan hasn't mastered Japanese, but she can communicate.
* Bill has still not arrived.
* The rain hasn't stopped.
TOPIC 5 Multiple Actions at Different Times
We also use the Present Perfect to talk about several different actions which have occurred in the past at different times. Present Perfect suggests the process is not complete and more actions are possible.
Examples:
* The army has attacked that city five times.
* I have had four quizzes and five tests so far this semester.
* We have had many major problems while working on this project.
* She has talked to several specialists about her problem, but nobody knows why she is sick.
Time Expressions with Present Perfect
When we use the Present Perfect it means that something has happened at some point in our lives before now. Remember, the exact time the action happened is not important.
Sometimes, we want to limit the time we are looking in for an experience. We can do this with expressions such as: in the last week, in the last year, this week, this month, so far, up to now, etc.
Examples:
* Have you been to Mexico in the last year?
* I have seen that movie six times in the last month.
* They have had three tests in the last week.
* She graduated from university less than three years ago. She has worked for three different companies so far.
* My car has broken down three times this week.
NOTICE
"Last year" and "in the last year" are very different in meaning. "Last year" means the year before now, and it is considered a specific time which requires Simple Past. "In the last year" means from 365 days ago until now. It is not considered a specific time, so it requires Present Perfect.
Examples:
* I went to Mexico last year.
I went to Mexico in the calendar year before this one.
* I have been to Mexico in the last year.
I have been to Mexico at least once at some point between 365 days ago and now.
USE 2 Duration From the Past Until Now (Non-Continuous Verbs)
With Non-Continuous Verbs and non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, we use the Present Perfect to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now. "For five minutes," "for two weeks," and "since Tuesday" are all durations which can be used with the Present Perfect.
Examples:
* I have had a cold for two weeks.
* She has been in England for six months.
* Mary has loved chocolate since she was a little girl.
Although the above use of Present Perfect is normally limited to Non-Continuous Verbs and non-continuous uses of Mixed Verbs, the words "live," "work," "teach," and "study" are sometimes used in this way even though they are NOT Non-Continuous Verbs.
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You have only seen that movie one time.
* Have you only seen that movie one time?
Examples:
* Many tourists have visited that castle. Active
* That castle has been visited by many tourists. Passive
Common Mistakes
Chinese Style: It's seven twenty o'clock.
American Style: It's seven twenty.
Chinese Style: Your coat is broken.
American Style: Your coat is torn.
Chinese Style: Susan didn't make a fault anyway.
American Style: Susan didn't make a mistake anyway.
Chinese Style: Would you mind posting this letter for me ? Yes, certainly.
American Style: Would you mind mailing this letter for me ? Of course not. OR ( Not at all )
Chinese Style: He becomes better.
American Style: He got better.
Chinese Style: We'll have a hearing test tomorrow.
American Style: We'll have a listening test tomorow.
Chinese Style: I recommend you to take a long vacation.
American Style: I recommend that you take a long vacation.
Chinese Style: The last bus leaves at eleven o'clock. It's about eleven now, Hurry up!
American Style: The last bus leaves at eleven o'clock. It's nearly ( almost ) eleven now, Hurry up!
Chinese Style: It was still bright outside.
American Style: It was still light outside.
Chinese Style: Come to here.
American Style: Come here.
Chinese Style: Common students in US don't wear a uniform.
American Style: The average students in US don't wear a uniform.
Chinese Style: Who cooked this salad ?
American Style: Who made this salad ?
Chinese Style: Different from me, she is proficient in English.
American Style: Unlike me, she is proficient in English.
Chinese Style: Little children are difficult to understand that.
American Style: It is difficult for children to understand that.
Chinese Style: Don't step on the grass.
American Style: Keep off the grass.
Chinese Style:I get my salary twice a month.
American Style: I get paid twice a month..
Chinese Style: Would you like a drink ?
American Style: Would you like something to drink ?
Chinese Style: Let me examine your pulse.
American Style: Let me feel your pulse.
Chinese Style: I have no exercise talent.
American Style: I am not athletic.
Chinese Style: Don't expect me too much.
American Style: Don't expect too much from (of ) me.
Chinese Style: I know his face.
American Style: I know him by sight.
Chinese Style:I forget my hat in the house.
American Style: I left my hat in the house.
Chinese Style:Lend me some money, for instance 500 dollars, Lin
American Style Lend me some money, say 500 dollars, Lin
Chinese Style: I have a free time.
American Style:I am free.
Chinese Style:The sun rises from the East.
American Style: The sun rises in the East.
Chinese Style:The thief got in from the window.
American Style: The thief got in through the window.
To view more click here
American Style: It's seven twenty.
Chinese Style: Your coat is broken.
American Style: Your coat is torn.
Chinese Style: Susan didn't make a fault anyway.
American Style: Susan didn't make a mistake anyway.
Chinese Style: Would you mind posting this letter for me ? Yes, certainly.
American Style: Would you mind mailing this letter for me ? Of course not. OR ( Not at all )
Chinese Style: He becomes better.
American Style: He got better.
Chinese Style: We'll have a hearing test tomorrow.
American Style: We'll have a listening test tomorow.
Chinese Style: I recommend you to take a long vacation.
American Style: I recommend that you take a long vacation.
Chinese Style: The last bus leaves at eleven o'clock. It's about eleven now, Hurry up!
American Style: The last bus leaves at eleven o'clock. It's nearly ( almost ) eleven now, Hurry up!
Chinese Style: It was still bright outside.
American Style: It was still light outside.
Chinese Style: Come to here.
American Style: Come here.
Chinese Style: Common students in US don't wear a uniform.
American Style: The average students in US don't wear a uniform.
Chinese Style: Who cooked this salad ?
American Style: Who made this salad ?
Chinese Style: Different from me, she is proficient in English.
American Style: Unlike me, she is proficient in English.
Chinese Style: Little children are difficult to understand that.
American Style: It is difficult for children to understand that.
Chinese Style: Don't step on the grass.
American Style: Keep off the grass.
Chinese Style:I get my salary twice a month.
American Style: I get paid twice a month..
Chinese Style: Would you like a drink ?
American Style: Would you like something to drink ?
Chinese Style: Let me examine your pulse.
American Style: Let me feel your pulse.
Chinese Style: I have no exercise talent.
American Style: I am not athletic.
Chinese Style: Don't expect me too much.
American Style: Don't expect too much from (of ) me.
Chinese Style: I know his face.
American Style: I know him by sight.
Chinese Style:I forget my hat in the house.
American Style: I left my hat in the house.
Chinese Style:Lend me some money, for instance 500 dollars, Lin
American Style Lend me some money, say 500 dollars, Lin
Chinese Style: I have a free time.
American Style:I am free.
Chinese Style:The sun rises from the East.
American Style: The sun rises in the East.
Chinese Style:The thief got in from the window.
American Style: The thief got in through the window.
To view more click here
Present Continuous
[am/is/are + present participle]
Examples:
* You are watching TV.
* Are you watching TV?
* You are not watching TV.
USE 1 Now

Use the Present Continuous with Normal Verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now.
Examples:
* You are learning English now.
* You are not swimming now.
* Are you sleeping?
* I am sitting.
* I am not standing.
* Is he sitting or standing?
* They are reading their books.
* They are not watching television.
* What are you doing?
* Why aren't you doing your homework?
USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now

In English, "now" can mean: this second, today, this month, this year, this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the Present Continuous to say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second.
Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while eating dinner in a restaurant.)
* I am studying to become a doctor.
* I am not studying to become a dentist.
* I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
* I am not reading any books right now.
* Are you working on any special projects at work?
* Aren't you teaching at the university now?
USE 3 Near Future
Sometimes, speakers use the Present Continuous to indicate that something will or will not happen in the near future.
Examples:
* I am meeting some friends after work.
* I am not going to the party tonight.
* Is he visiting his parents next weekend?
* Isn't he coming with us tonight?
USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with "Always"
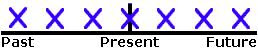
The Present Continuous with words such as "always" or "constantly" expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happens. Notice that the meaning is like Simple Present, but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words "always" or "constantly" between "be" and "verb+ing."
Examples:
* She is always coming to class late.
* He is constantly talking. I wish he would shut up.
* I don't like them because they are always complaining.
REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs/ Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Present Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Present.
Examples:
* She is loving this chocolate ice cream. Not Correct
* She loves this chocolate ice cream. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You are still watching TV.
* Are you still watching TV?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Right now, Tom is writing the letter. Active
* Right now, the letter is being written by Tom. Passive
Video
Examples:
* You are watching TV.
* Are you watching TV?
* You are not watching TV.
USE 1 Now

Use the Present Continuous with Normal Verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now.
Examples:
* You are learning English now.
* You are not swimming now.
* Are you sleeping?
* I am sitting.
* I am not standing.
* Is he sitting or standing?
* They are reading their books.
* They are not watching television.
* What are you doing?
* Why aren't you doing your homework?
USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now

In English, "now" can mean: this second, today, this month, this year, this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the Present Continuous to say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second.
Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while eating dinner in a restaurant.)
* I am studying to become a doctor.
* I am not studying to become a dentist.
* I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
* I am not reading any books right now.
* Are you working on any special projects at work?
* Aren't you teaching at the university now?
USE 3 Near Future

Sometimes, speakers use the Present Continuous to indicate that something will or will not happen in the near future.
Examples:
* I am meeting some friends after work.
* I am not going to the party tonight.
* Is he visiting his parents next weekend?
* Isn't he coming with us tonight?
USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with "Always"

The Present Continuous with words such as "always" or "constantly" expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happens. Notice that the meaning is like Simple Present, but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words "always" or "constantly" between "be" and "verb+ing."
Examples:
* She is always coming to class late.
* He is constantly talking. I wish he would shut up.
* I don't like them because they are always complaining.
REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs/ Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Present Continuous with these verbs, you must use Simple Present.
Examples:
* She is loving this chocolate ice cream. Not Correct
* She loves this chocolate ice cream. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You are still watching TV.
* Are you still watching TV?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Right now, Tom is writing the letter. Active
* Right now, the letter is being written by Tom. Passive
Video
Simple Present
[VERB] + s/es in third person
Examples:
* You speak English.
* Do you speak English?
* You do not speak English.
USE 1 Repeated Actions
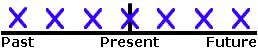
Use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do.
Examples:
* I play tennis.
* She does not play tennis.
* Does he play tennis?
* The train leaves every morning at 8 AM.
* The train does not leave at 9 AM.
* When does the train usually leave?
* She always forgets her purse.
* He never forgets his wallet.
* Every twelve months, the Earth circles the Sun.
* Does the Sun circle the Earth?
USE 2 Facts or Generalizations

The Simple Present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true now, and will be true in the future. It is not important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is also used to make generalizations about people or things.
Examples:
* Cats like milk.
* Birds do not like milk.
* Do pigs like milk?
* California is in America.
* California is not in the United Kingdom.
* Windows are made of glass.
* Windows are not made of wood.
* New York is a small city. It is not important that this fact is untrue.
USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future
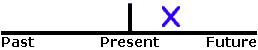
Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events as well.
Examples:
* The train leaves tonight at 6 PM.
* The bus does not arrive at 11 AM, it arrives at 11 PM.
* When do we board the plane?
* The party starts at 8 o'clock.
* When does class begin tomorrow?
USE 4 Now (Non-Continuous Verbs)

Speakers sometimes use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is happening or is not happening now. This can only be done with Non-Continuous Verbs and certain Mixed Verbs.
Examples:
* I am here now.
* She is not here now.
* He needs help right now.
* He does not need help now.
* He has his passport in his hand.
* Do you have your passport with you?
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You only speak English.
* Do you only speak English?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Once a week, Tom cleans the car. Active
* Once a week, the car is cleaned by Tom. Passive
More About Active / Passive Forms
Video
Video 1
Viveo 2
Exercises and Related Topics
* Verb Tense Exercise 1 Simple Present and Present Continuous
* Verb Tense Practice Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
* Verb Tense Final Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
Examples:
* You speak English.
* Do you speak English?
* You do not speak English.
USE 1 Repeated Actions

Use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do.
Examples:
* I play tennis.
* She does not play tennis.
* Does he play tennis?
* The train leaves every morning at 8 AM.
* The train does not leave at 9 AM.
* When does the train usually leave?
* She always forgets her purse.
* He never forgets his wallet.
* Every twelve months, the Earth circles the Sun.
* Does the Sun circle the Earth?
USE 2 Facts or Generalizations

The Simple Present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true now, and will be true in the future. It is not important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is also used to make generalizations about people or things.
Examples:
* Cats like milk.
* Birds do not like milk.
* Do pigs like milk?
* California is in America.
* California is not in the United Kingdom.
* Windows are made of glass.
* Windows are not made of wood.
* New York is a small city. It is not important that this fact is untrue.
USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future

Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events as well.
Examples:
* The train leaves tonight at 6 PM.
* The bus does not arrive at 11 AM, it arrives at 11 PM.
* When do we board the plane?
* The party starts at 8 o'clock.
* When does class begin tomorrow?
USE 4 Now (Non-Continuous Verbs)

Speakers sometimes use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is happening or is not happening now. This can only be done with Non-Continuous Verbs and certain Mixed Verbs.
Examples:
* I am here now.
* She is not here now.
* He needs help right now.
* He does not need help now.
* He has his passport in his hand.
* Do you have your passport with you?
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You only speak English.
* Do you only speak English?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Once a week, Tom cleans the car. Active
* Once a week, the car is cleaned by Tom. Passive
More About Active / Passive Forms
Video
Video 1
Viveo 2
Exercises and Related Topics
* Verb Tense Exercise 1 Simple Present and Present Continuous
* Verb Tense Practice Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
* Verb Tense Final Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
Past Perfect Continuous
FORM
[had been + present participle]
Examples:
* You had been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived.
* Had you been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived?
* You had not been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived.
USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Past

We use the Past Perfect Continuous to show that something started in the past and continued up until another time in the past. "For five minutes" and "for two weeks" are both durations which can be used with the Past Perfect Continuous. Notice that this is related to the Present Perfect Continuous; however, the duration does not continue until now, it stops before something else in the past.
Examples:
* They had been talking for over an hour before Tony arrived.
* She had been working at that company for three years when it went out of business.
* How long had you been waiting to get on the bus?
* Mike wanted to sit down because he had been standing all day at work.
* James had been teaching at the university for more than a year before he left for Asia.
* A: How long had you been studying Turkish before you moved to Ankara?
* B:I had not been studying Turkish very long.
USE 2 Cause of Something in the Past

Using the Past Perfect Continuous before another action in the past is a good way to show cause and effect.
Examples:
* Jason was tired because he had been jogging.
* Sam gained weight because he had been overeating.
* Betty failed the final test because she had not been attending class.
Past Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous
If you do not include a duration such as "for five minutes," "for two weeks" or "since Friday," many English speakers choose to use the Past Continuous rather than the Past Perfect Continuous. Be careful because this can change the meaning of the sentence. Past Continuous emphasizes interrupted actions, whereas Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes a duration of time before something in the past. Study the examples below to understand the difference.
Examples:
* He was tired because he was exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he was tired because he was exercising at that exact moment.
* He was tired because he had been exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he was tired because he had been exercising over a period of time. It is possible that he was still exercising at that moment OR that he had just finished.
REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Past Perfect Continuous with these verbs, you must use Past Perfect.
Examples:
* The motorcycle had been belonging to George for years before Tina bought it. Not Correct
* The motorcycle had belonged to George for years before Tina bought it. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You had only been waiting there for a few minutes when she arrived.
* Had you only been waiting there for a few minutes when she arrived?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Chef Jones had been preparing the restaurant's fantastic dinners for two years before he moved to Paris. Active
* The restaurant's fantastic dinners had been being prepared by Chef Jones for two years before he moved to Paris. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Past Perfect Continuous are not common.
More About Active / Passive Forms
EXERCISES AND RELATED TOPICS
* Verb Tense Exercise 13 Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous
[had been + present participle]
Examples:
* You had been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived.
* Had you been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived?
* You had not been waiting there for more than two hours when she finally arrived.
USE 1 Duration Before Something in the Past

We use the Past Perfect Continuous to show that something started in the past and continued up until another time in the past. "For five minutes" and "for two weeks" are both durations which can be used with the Past Perfect Continuous. Notice that this is related to the Present Perfect Continuous; however, the duration does not continue until now, it stops before something else in the past.
Examples:
* They had been talking for over an hour before Tony arrived.
* She had been working at that company for three years when it went out of business.
* How long had you been waiting to get on the bus?
* Mike wanted to sit down because he had been standing all day at work.
* James had been teaching at the university for more than a year before he left for Asia.
* A: How long had you been studying Turkish before you moved to Ankara?
* B:I had not been studying Turkish very long.
USE 2 Cause of Something in the Past

Using the Past Perfect Continuous before another action in the past is a good way to show cause and effect.
Examples:
* Jason was tired because he had been jogging.
* Sam gained weight because he had been overeating.
* Betty failed the final test because she had not been attending class.
Past Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous
If you do not include a duration such as "for five minutes," "for two weeks" or "since Friday," many English speakers choose to use the Past Continuous rather than the Past Perfect Continuous. Be careful because this can change the meaning of the sentence. Past Continuous emphasizes interrupted actions, whereas Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes a duration of time before something in the past. Study the examples below to understand the difference.
Examples:
* He was tired because he was exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he was tired because he was exercising at that exact moment.
* He was tired because he had been exercising so hard.
This sentence emphasizes that he was tired because he had been exercising over a period of time. It is possible that he was still exercising at that moment OR that he had just finished.
REMEMBER Non-Continuous Verbs / Mixed Verbs
It is important to remember that Non-Continuous Verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for Mixed Verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using Past Perfect Continuous with these verbs, you must use Past Perfect.
Examples:
* The motorcycle had been belonging to George for years before Tina bought it. Not Correct
* The motorcycle had belonged to George for years before Tina bought it. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as: always, only, never, ever, still, just, etc.
Examples:
* You had only been waiting there for a few minutes when she arrived.
* Had you only been waiting there for a few minutes when she arrived?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
Examples:
* Chef Jones had been preparing the restaurant's fantastic dinners for two years before he moved to Paris. Active
* The restaurant's fantastic dinners had been being prepared by Chef Jones for two years before he moved to Paris. Passive
NOTE: Passive forms of the Past Perfect Continuous are not common.
More About Active / Passive Forms
EXERCISES AND RELATED TOPICS
* Verb Tense Exercise 13 Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)